An overview of the Middle East and North Africa region
 At the beginning of 2020, the Arab countries were subjected to two major shocks; the first shock was the Coronavirus pandemic, and the subsequent economic effects like the rest of the world, while the second shock was the drop in oil prices. These two shocks caused an economic contraction in 2020 by about 4.2%, according to the International Monetary Fund data.
At the beginning of 2020, the Arab countries were subjected to two major shocks; the first shock was the Coronavirus pandemic, and the subsequent economic effects like the rest of the world, while the second shock was the drop in oil prices. These two shocks caused an economic contraction in 2020 by about 4.2%, according to the International Monetary Fund data.
Which made countries take several economic measures and procedures to confront the pandemic by redirecting part of the general budget to the health sector and supporting the economic activities affected by the pandemic, as the additional amount of cash elevated by the central banks amounted to about 3.4% of the Gross Domestic Production.
The industrial sector incurred significant economic losses in the light of the precautionary measures for the pandemic, such as the curfew, the cut of workers number present, the drop in demand, and the contraction in international trade movement.
The steel sector came at the lead of these industries and the most affected, noting that dozens of other industries such as urbanization, building, construction, automobiles, aircraft, ships, railways, and others depend on this industry.
The recession included all factories without exception, whether integrated or semi-integrated or rolling mills, due to the suspension of most projects except for the huge government ones.
Figures and evidence indicate that the steel sector with all its products and types, whether raw steel or billets or the final products of steel plates, and reinforcing bar has been affected, and we can divide this period into two phases:
- The first stage: the beginning of 2020 with the beginning of the spread of the Coronavirus pandemic until November
Since the Coronavirus pandemic outbreak, the steel sector has met great obstacles. Their indications varied within a severe slowdown in the production discharge due to the decline in the sea movement, air, and land transportation on one hand, as well as a decline in steel consumption owing to the halt of most projects, except the large government projects ones, on the other hand.
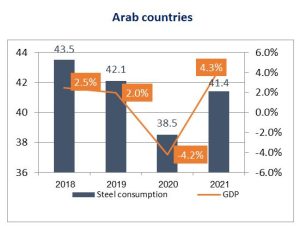
The consumption of long products and hot-steel plates decreased by -9% to reach 38.5 million tonnes, a drop of about 3.6 million tonnes from 2019, which led to a contraction in production in some plants and stoppage of others, as a result of a notable decline in sales.
The second stage: The start of the recovery of economic activity and the rise in oil prices from late 2020 until the present time.
With the countries driving to ease precautionary measures and a relative return to economic activity, along with the discovery of the anti-pandemic vaccine, and the start of providing anti-Coronavirus vaccine doses of all kinds, this led to an acceleration in economic growth rates in most countries of the world. With a recovery in oil prices, the International Monetary Fund raised expectations in rate growth to 4.3% in the Arab region in 2021, after a contraction period that amounted to -4.2% in 2020.
The World Steel Organization expected that global steel demand would recover to reach 1795.1 million tonnes in 2021, an increase of 4.1%, with a gradual return of activities and mega projects undertaken by governments. As for the Arab region, the growth rate of steel consumption is expected to 8% to reach 41.3 million tonnes, an increase of 2.8 million tonnes.